Saturday, 29 July 2017
FOR DESIGN OF MANUAL BOOKS OF THE ANY MACHINE
Contact these number for Tanzania and any Country
+255765281915
or email: malemahmalema@gmail.com
or
engmalemahmalema@gmail.com
Thursday, 25 May 2017
18 Mechanical Properties Which Every Mechanical Engineer Should Know
Material selection for any product is main part of a manufacturing industries. The quality of product is highly depends upon its material properties. These properties are used to distinguish materials from each other. For Example: A harder material is used to make tools.A ductile material is used to draw wires. So the knowledge of mechanical properties of material is desirable for any mechanical student or for any person belongs to mechanical industries. This article brings top 18 mechanical properties. I hope you will like it.
Mechanical properties of material:
There are mainly two types of materials. First one is metal and other one is non metals. Metals are classified into two types : Ferrous metals and Non-ferrous metals.
Ferrous metals mainly consist iron with comparatively small addition of other materials. It includes iron and its alloy such as cast iron, steel, HSS etc. Ferrous metals are widely used in mechanical industries for its various advantages.
Nonferrous metals contain little or no iron. It includes aluminum, magnesium, copper, zinc etc.
Most Mechanical properties are associated with metals. These are
#1. Strength:
The ability of material to withstand load without failure is known as strength. If a material can bear more load, it means it has more strength. Strength of any material mainly depends on type of loading and deformation before fracture. According to loading types, strength can be classified into three types.
- a. Tensile strength:
- b. Compressive strength:
- 3. Shear strength:
According to the deformation before fracture, strength can be classified into three types.
- a. Elastic strength:
- b. Yield strength:
- c. Ultimate strength:
#2. Homogeneity:
If a material has same properties throughout its geometry, known as homogeneous material and the property is known as homogeneity. It is an ideal situation but practically no material is homogeneous.
#3. Isotropy:
A material which has same elastic properties along its all loading direction known as isotropic material.
#4. Anisotropy:
A material which exhibits different elastic properties in different loading direction known as an-isotropic material.
#5. Elasticity:
If a material regain its original dimension after removal of load, it is known as elastic material and the property by virtue of which it regains its original shape is known as elasticity.
Every material possess some elasticity. It is measure as the ratio of stress to strain under elastic limit.
#6. Plasticity:
The ability of material to undergo some degree of permanent deformation without failure after removal of load is known as plasticity. This property is used for shaping material by metal working. It is mainly depends on temperature and elastic strength of material.
#7. Ductility:
Ductility is a property by virtue of which metal can be drawn into wires. It can also define as a property which permits permanent deformation before fracture under tensile loading. The amount of permanent deformation (measure in percentage elongation) decides either the material is ductile or not.
Percentage elongation = (Final Gauge Length – Original Gauge Length )*100/ Original Gauge Length
If the percentage elongation is greater than 5% in a gauge length 50 mm, the material is ductile and if it less than 5% it is not.
#8. Brittleness:
Brittleness is a property by virtue of which, a material will fail under loading without significant change in dimension. Glass and cast iron are well known brittle materials.
#9. Stiffness:
The ability of material to resist elastic deformation or deflection during loading, known as stiffness. A material which offers small change in dimension during loading is more stiffer. For example steel is stiffer than aluminum.
#10. Hardness:
The property of a material to resist penetration is known as hardness. It is an ability to resist scratching, abrasion or cutting.
It is also define as an ability to resist fracture under point loading.
#11. Toughness:
Toughness is defined as an ability to withstand with plastic or elastic deformation without failure. It is defined as the amount of energy absorbed before actual fracture.
#12. Malleability:
A property by virtue of which a metal can flatten into thin sheets, known as malleability. It is also define as a property which permits plastic deformation under compression loading.
#13. Machinability:
A property by virtue of which a material can be cut easily.
#14. Damping:
The ability of metal to dissipate the energy of vibration or cyclic stress is called damping. Cast iron has good damping property, that’s why most of machines body made by cast iron.
#15. Creep:
The slow and progressive change in dimension of a material under influence of its safe working stress for long time is known as creep. Creep is mainly depend on time and temperature. The maximum amount of stress under which a material withstand during infinite time is known as creep strength.
#16. Resilience:
The amount of energy absorb under elastic limit during loading is called resilience. The maximum amount of the energy absorb under elastic limit is called proof resilience.
#17. Fatigue Strength:
The failure of a work piece under cyclic load or repeated load below its ultimate limit is known as fatigue. The maximum amount of cyclic load which a work piece can bear for infinite number of cycle is called fatigue strength. Fatigue strength is also depend on work piece shape, geometry, surface finish etc.
#18. Embrittlement:
The loss of ductility of a metal caused by physical or chemical changes, which make it brittle, is called embrittlement.
Wednesday, 3 May 2017
Tuesday, 2 May 2017
TEN PRINCIPLES FOR GOOD MACHINE DESIGN
- Good design is innovative.
- Good design makes a product useful.
- Good design is aesthetic.
- Good design makes a product understandable.
- Good design is unobtrusive.
- Good design is honest.
- Good design is long-lasting.
- Good design is thorough down to the last detail.
- Good design is environmentally friendly.
- Good design is as little design as possible.
Monday, 1 May 2017
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN AUTOCAD AND SOLIDWORKS
SolidWorks is what we call a "parametric" solid modeller used for 3-D design. Parametric means that the dimensions can have relationships between one another and can be changed at any point during the design process to automatically alter the solid part and any related documentation (blueprint). AutoCAD, however, is primarily a 2-D design tool with some, but limited 3-D capabilities. It is very simple compared to any parametric solid modeller (although 3D is improved in AutoCAD 2007). Autodesk (the manufacturer of AutoCAD) makes a product that is nearly identical to SolidWorks, called Inventor, which is a parametric program for design of solid parts and assemblies.
SolidWorks is a 3D mechanical CAD (computer-aided design) program that runs on Microsoft Windows. SolidWorks files use the Microsoft Structured storage file format. This means that there is various files embedded within each SLDDRW (drawing files), SLDPRT (part files), SLDASM (assembly files), with preview bitmaps and metadata sub-files. Various third-party tools can be used to extract these sub-files, although the sub-files in many cases use proprietary binary file formats. SolidWorks is a parasolid-based solid modeller, and utilizes a parametric feature-based approach to create models and assemblies. Parameters refer to restrictions which values determine the shape or geometry of the model. Parameters can be either numeric, such as line lengths or circle diameters, or geometric, such as tangent, parallel, concentric, horizontal or vertical. Numeric parameters can be associated with each other through the use of relations, which allows them to capture design intent.
SolidWorks is a 3D mechanical CAD (computer-aided design) program that runs on Microsoft Windows. SolidWorks files use the Microsoft Structured storage file format. This means that there is various files embedded within each SLDDRW (drawing files), SLDPRT (part files), SLDASM (assembly files), with preview bitmaps and metadata sub-files. Various third-party tools can be used to extract these sub-files, although the sub-files in many cases use proprietary binary file formats. SolidWorks is a parasolid-based solid modeller, and utilizes a parametric feature-based approach to create models and assemblies. Parameters refer to restrictions which values determine the shape or geometry of the model. Parameters can be either numeric, such as line lengths or circle diameters, or geometric, such as tangent, parallel, concentric, horizontal or vertical. Numeric parameters can be associated with each other through the use of relations, which allows them to capture design intent.
AutoCAD is, just like SolidWorks, a Computer Aided Design software application for 2-D and 3-D design and drafting. AutoCAD was one of the first CAD programs to run on personal or home computers, notably the IBM personal computer. At that time, most other CAD programs ran on mainframe computers or mini-computers that were connected to a graphics computer terminal for each user. Early releases of AutoCAD used basic entities such as lines, poly-lines, circles, arcs, and text to ultimately construct more complex objects. AutoCAD has since started to support custom objects through its C++ Application Programming Interface (API).
Modern AutoCAD includes a full set of basic solid modelling and 3-D tools. With the release of AutoCAD 2007 improved 3D modelling saw the light, which means better navigation when working in three dimensions. It also became easier to edit 3-D models. The mental ray engine was included in rendering and thus it was now possible to do quality renderings. AutoCAD 2010 introduced parametric functionality and network modelling. At this moment, AutoCAD only runs under Microsoft Windows operating systems. It is available in 32-bit and 64-bit versions. AutoCAD can run on an emulator or compatibility layer like VM-ware Workstation or Wine, although various performance issues can arise if you work with 3-D objects or large drawings.
Choosing a system that works for you depends solely on the type of work you want to do. Many experts say that SolidWorks is more effective when working on 3 dimensional designs and that AutoCAD is the way to go for 2 dimensional design.
Modern AutoCAD includes a full set of basic solid modelling and 3-D tools. With the release of AutoCAD 2007 improved 3D modelling saw the light, which means better navigation when working in three dimensions. It also became easier to edit 3-D models. The mental ray engine was included in rendering and thus it was now possible to do quality renderings. AutoCAD 2010 introduced parametric functionality and network modelling. At this moment, AutoCAD only runs under Microsoft Windows operating systems. It is available in 32-bit and 64-bit versions. AutoCAD can run on an emulator or compatibility layer like VM-ware Workstation or Wine, although various performance issues can arise if you work with 3-D objects or large drawings.
Choosing a system that works for you depends solely on the type of work you want to do. Many experts say that SolidWorks is more effective when working on 3 dimensional designs and that AutoCAD is the way to go for 2 dimensional design.
Monday, 30 January 2017
Where do we use leaf spring ? What is special about leaf spring?
January 30, 2017
No comments
Q Where do we use leaf spring ? List down the applications of leaf spring. What is special about leaf spring?
- You can answer this question.
- You can like the best answer
- You can share the question
- You can get updates of new questions on Facebook
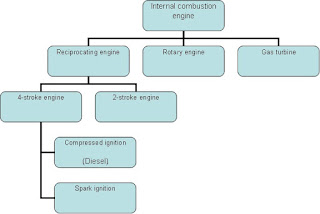
List down the ways the classification of IC Engine can be done
January 30, 2017
No comments
List down the ways the classification of IC Engine can be done
You can answer this question.
You can like the best answer.
You can share the question
You can get updates of new questions on Facebook
You can answer this question.
Why sectional view is used in machine drawing? What is full section and what is half section?
January 30, 2017
2 comments
Sunday, 29 January 2017
What is Assembly Drawing and why do we need them?
January 29, 2017
No comments
Monday, 23 January 2017
Tuesday, 13 September 2016
Drawings Graphics Language
Sample of engineering Design Drawings
1.General:A technical person can use the graphic language as powerful means of communication with others for conveying ideas on technical matters. However, for effective exchange of ideas with others, the engineer must have proficiency in
(i) language, both written and oral,
(ii) symbols associated with basic sciences and
(iii) the graphic language. Engineering drawing is a suitable graphic language from which any trained person can visualise the required object.
As an engineering drawing displays the exact picture of an object, it obviously conveys the same ideas to every trained eye. Irrespective of language barriers, the drawings can be effectively used in other countries, in addition to the country where they are prepared. Thus, the engineering drawing is the universal language of all engineers. Engineering drawing has its origin sometime in 500 BC in the regime of King Pharos of Egypt when symbols were used to convey the ideas among people.
2.Importance Of Graphics Language: The graphic language had its existence when it became necessary to build new structures and create new machines or the like, in addition to representing the existing ones. In the absence of graphic language, the ideas on technical matters have to be conveyed by speech or writing, both are unreliable and difficult to understand by the shop floor people for manufacturing. This method involves not only lot of time and labour, but also manufacturing errors. Without engineering drawing, it would have been impossible to produce objects such as aircrafts, automobiles, locomotives, etc., each requiring thousands of different components.
3.Need For Correct Drawings: The drawings prepared by any technical person must be clear, unmistakable in meaning and there should not be any scope for more than one interpretation, or else litigation may arise. In a number of dealings with contracts, the drawing is an official document and the success or failure of a structure depends on the clarity of details provided on the drawing. Thus, the drawings should not give any scope for mis-interpretation even by accident. It would not have been possible to produce the machines/automobiles on a mass scale where a number of assemblies and sub-assemblies are involved, without clear, correct and accurate drawings. To achieve this, the technical person must gain a thorough knowledge of both the principles and conventional practice of draughting. If these are not achieved and or practiced, the drawings prepared by one may convey different meaning to others, causing unnecessary delays and expenses in production shops. Hence, an engineer should posses good knowledge, not only in preparing a correct drawing but also to read the drawing correctly. The course content of this book is expected to meet these requirements. The study of machine drawing mainly involves learning to sketch machine parts and to make working and assembly drawings. This involves a study of those conventions in drawings that are widely adopted in engineering practice.
Monday, 12 September 2016
Part Mode, Assembly Mode And Drawing Mode In Solidworks 2016
Part Mode
The Part mode of SOLIDWORKS is a feature-based parametric environment in which you can create solid models. In this mode, you are provided with three default planes named as Front Plane, Top Plane, and Right Plane. First, you need to select a sketching plane to create a sketch for the base feature. On selecting a sketching plane, you enter the sketching environment. The sketches for the model are drawn in the sketching environment using easy-to-use tools. After drawing the sketches, you can dimension them and apply the required relations in the same sketching environment. The design intent is captured easily by adding relations and equations and using the design table in the design. You are provided with the standard hole library known as the Hole Wizard in the Part mode. You can create simple holes, tapped holes, counterbore holes, countersink holes, and so on by using this wizard. The holes can be of any standard such as ISO, ANSI, JIS, and so on. You can also create complicated surfaces by using the surface modeling tools available in the Part mode. Annotations such as weld symbols, geometric tolerance, datum references, and surface finish symbols can be added to the model within the Part mode. The standard features that are used frequently can be saved as library features and retrieved when needed. The palette feature library of SOLIDWORKS contains a number of standard mechanical parts and features. You can also create the sheet metal components in this mode of SOLIDWORKS by using the related tools. Besides this, you can also analyze the part model for various stresses applied to it in the real physical conditions by using an easy and userfriendly tool called SimulationXpress. It helps you reduce the cost and time in physically testing your design in real testing conditions (destructive tests). You can also analyze the component during modeling in the SOLIDWORKS windows. In addition, you can work with the weld modeling within the Part mode of SOLIDWORKS by creating steel structures and adding weld beads. All standard weld types and welding conditions are available for your reference. You can extract the core and the cavity in the Part mode by using the mold design tools.
Assembly Mode
The Part mode of SOLIDWORKS is a feature-based parametric environment in which you can create solid models. In this mode, you are provided with three default planes named as Front Plane, Top Plane, and Right Plane. First, you need to select a sketching plane to create a sketch for the base feature. On selecting a sketching plane, you enter the sketching environment. The sketches for the model are drawn in the sketching environment using easy-to-use tools. After drawing the sketches, you can dimension them and apply the required relations in the same sketching environment. The design intent is captured easily by adding relations and equations and using the design table in the design. You are provided with the standard hole library known as the Hole Wizard in the Part mode. You can create simple holes, tapped holes, counterbore holes, countersink holes, and so on by using this wizard. The holes can be of any standard such as ISO, ANSI, JIS, and so on. You can also create complicated surfaces by using the surface modeling tools available in the Part mode. Annotations such as weld symbols, geometric tolerance, datum references, and surface finish symbols can be added to the model within the Part mode. The standard features that are used frequently can be saved as library features and retrieved when needed. The palette feature library of SOLIDWORKS contains a number of standard mechanical parts and features. You can also create the sheet metal components in this mode of SOLIDWORKS by using the related tools. Besides this, you can also analyze the part model for various stresses applied to it in the real physical conditions by using an easy and userfriendly tool called SimulationXpress. It helps you reduce the cost and time in physically testing your design in real testing conditions (destructive tests). You can also analyze the component during modeling in the SOLIDWORKS windows. In addition, you can work with the weld modeling within the Part mode of SOLIDWORKS by creating steel structures and adding weld beads. All standard weld types and welding conditions are available for your reference. You can extract the core and the cavity in the Part mode by using the mold design tools.
Assembly Mode
In the Assembly mode, you can assemble components of the assembly with the help of the required tools. There are two methods of assembling the components:
1. Bottom-up assembly
2. Top-down assembly
In the bottom-up assembly method, the assembly is created by assembling the components created earlier and maintaining their design intent. In the top-down method, the components are created in the assembly mode. You may begin with some ready-made parts and then create other components in the
context of the assembly. You can refer to the features of some components of the assembly to drive the dimensions of other components. You can assemble all components of an assembly by using a single tool, the Mate tool. While assembling the components of an assembly, you can also animate
the assembly by dragging. Besides this, you can also check the working of your assembly. Collision
detection is one of the important features in this mode. Using this feature, you can rotate and move
components as well as detect the interference and collision between the assembled components. You
can see the realistic motion of the assembly by using physical dynamics. Physical simulation is used
to simulate the assembly with the effects of motors, springs, and gravity on the assemblies.
Drawing Mode
The Drawing mode is used for the documentation of the parts or the assemblies created earlier in the
form of drawing views. The procedure for creating drawing views is called drafting. There are two
types of drafting done in SOLIDWORKS:
1. Generative drafting
2. Interactive drafting
Generative drafting is a process of generating drawing views of a part or an assembly created earlier.
The parametric dimensions and the annotations added to the component in the Part mode can be
generated in the drawing views. Generative drafting is bidirectionally associative in nature. Automatic
BOMs and balloons can be added to an assembly while generating the drawing views of it.
In interactive drafting, you have to create the drawing views by sketching them using normal
sketching tools and then add dimensions to them.
1. Bottom-up assembly
2. Top-down assembly
In the bottom-up assembly method, the assembly is created by assembling the components created earlier and maintaining their design intent. In the top-down method, the components are created in the assembly mode. You may begin with some ready-made parts and then create other components in the
context of the assembly. You can refer to the features of some components of the assembly to drive the dimensions of other components. You can assemble all components of an assembly by using a single tool, the Mate tool. While assembling the components of an assembly, you can also animate
the assembly by dragging. Besides this, you can also check the working of your assembly. Collision
detection is one of the important features in this mode. Using this feature, you can rotate and move
components as well as detect the interference and collision between the assembled components. You
can see the realistic motion of the assembly by using physical dynamics. Physical simulation is used
to simulate the assembly with the effects of motors, springs, and gravity on the assemblies.
Drawing Mode
The Drawing mode is used for the documentation of the parts or the assemblies created earlier in the
form of drawing views. The procedure for creating drawing views is called drafting. There are two
types of drafting done in SOLIDWORKS:
1. Generative drafting
2. Interactive drafting
Generative drafting is a process of generating drawing views of a part or an assembly created earlier.
The parametric dimensions and the annotations added to the component in the Part mode can be
generated in the drawing views. Generative drafting is bidirectionally associative in nature. Automatic
BOMs and balloons can be added to an assembly while generating the drawing views of it.
In interactive drafting, you have to create the drawing views by sketching them using normal
sketching tools and then add dimensions to them.
INTRODUCTION TO SOLIDWORKS 2016
Welcome to the world of Computer Aided Design (CAD) with SOLIDWORKS. If you are a new user
of this software package, you will be joining hands with thousands of users of this parametric, feature-based, and one of the most user-friendly software packages. If you are familiar with the previous releases of this software, you will be able to upgrade your designing skills with this improved release of SOLIDWORKS.
SOLIDWORKS, developed by the SOLIDWORKS Corporation, USA, is a feature-based, parametric
solid-modeling mechanical design and automation software. SOLIDWORKS is the first CAD package
to use the Microsoft Windows graphic user interface. The use of the drag and drop (DD) functionality
of Windows makes this CAD package extremely easy to learn. The Windows graphic user interface makes it possible for the mechanical design engineers to innovate their ideas and implement them in
the form of virtual prototypes or solid models, large assemblies, subassemblies, and detailing and
drafting.
of this software package, you will be joining hands with thousands of users of this parametric, feature-based, and one of the most user-friendly software packages. If you are familiar with the previous releases of this software, you will be able to upgrade your designing skills with this improved release of SOLIDWORKS.
SOLIDWORKS, developed by the SOLIDWORKS Corporation, USA, is a feature-based, parametric
solid-modeling mechanical design and automation software. SOLIDWORKS is the first CAD package
to use the Microsoft Windows graphic user interface. The use of the drag and drop (DD) functionality
of Windows makes this CAD package extremely easy to learn. The Windows graphic user interface makes it possible for the mechanical design engineers to innovate their ideas and implement them in
the form of virtual prototypes or solid models, large assemblies, subassemblies, and detailing and
drafting.
SOLIDWORKS is one of the products of SOLIDWORKS Corporation, which is a part of Dassault
Systemes. SOLIDWORKS also works as platform software for a number of software. This implies
that you can also use other compatible software within the SOLIDWORKS window. There are a
number of software provided by the SOLIDWORKS Corporation, which can be used as add-ins with
SOLIDWORKS. Some of the software that can be used on SOLIDWORKS’s work platform are listed
below
Systemes. SOLIDWORKS also works as platform software for a number of software. This implies
that you can also use other compatible software within the SOLIDWORKS window. There are a
number of software provided by the SOLIDWORKS Corporation, which can be used as add-ins with
SOLIDWORKS. Some of the software that can be used on SOLIDWORKS’s work platform are listed
SOLIDWORKS Simulation SOLIDWORKS Toolbox PhotoView 360 CircuitWorks
SOLIDWORKS Plastics SOLIDWORKS Inspection TolAnalyst
As mentioned earlier, SOLIDWORKS is a parametric, feature-based, and easy-to-use mechanical
design automation software. It enables you to convert the basic 2D sketch into a solid model by using
simple but highly effective modeling tools. It also enables you to create the virtual prototype of a
sheet metal component and the flat pattern of the component. This helps you in the complete process
planning for designing and creating a press tool. SOLIDWORKS helps you to extract the core and the
cavity of a model that has to be molded or cast. With SOLIDWORKS, you can also create complex
parametric shapes in the form of surfaces. Some of the important modes of SOLIDWORKS are
discussed next.